Process
CRVS Process
This outlines the process from event occurrence to generating the legal and permanent record to certification
Event registration principles
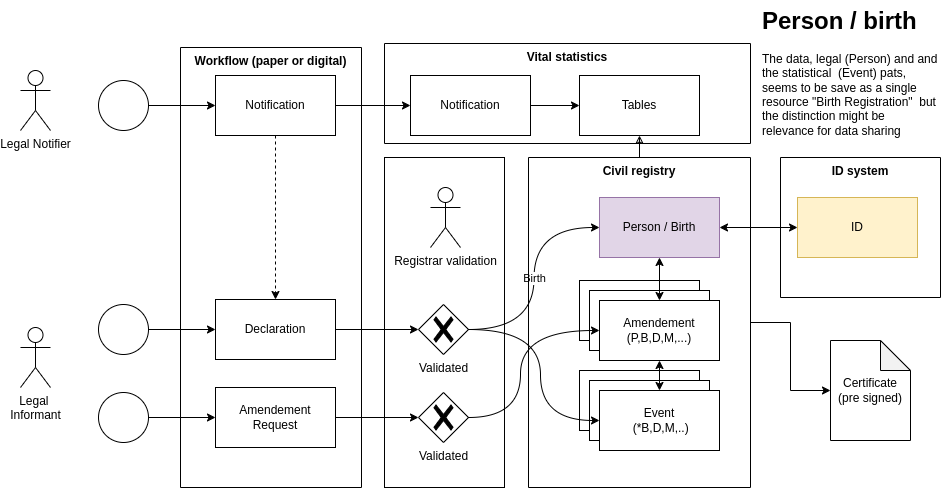
- Notifications: Providing the civil registrar with information about the occurrence of a birth or death (for example from the health sector), but the vital event cannot be registered based on this information alone; ideally processes should therefore be designed in a way that the issuance of proof of a birth or death (e.g., by the health sector) is combined with the Declaration step (see below) for that event.
- Declaration: Reporting all information necessary for the civil registration of an event by the legally designated informant (e.g., health sector staff, or mother and / or father#), upon which the civil registrar canmust register the events.
- Validation and Verification: Checking the accuracy of all the information that has been submitted about the occurrence of the vital event including verification of identities of the people involved in the registration process by linkage with the identity system and de-duplication.
- Registration: Creating the permanent legal record of the occurrence of the vital event for administrative, legal, and statistical purposes in the civil register.
- Certification: Issuance of certificates as proof of registration, using special paper or digital signatures. Issuing proof about the occurrence of the vital event in the form of a copy of all or part of the exact information contained on the original vital record. In manual or hybrid systems, in which not all registration centers are digitalized, the certificates can also be issued manually.
-
Electronic Storage: Storing and archiving of data.
-
Identity System Data Exchange and Synchronization: Updating the identity system with information on new birth and death to establish a new identity upon birth registration and retiring an identity upon death registration. This updated data is shared with other databases for administrative and service delivery purpose (i.e., updating the voter, social protection or tax registry).
- Data Sharing for Vital Statistics Production Making micro data (in real time or in batches) available to produce vital statistics.
- Archiving of Manual Records Archiving of physical records of the vital events.
Validation and data sharing
CRVS system could generate a qr code that will host some or all the data related to the Civil registration, this could be printed to any certificate in order to have a scannable version of the certificate or to carry one's civil registration record across border (regional, national, .. )
The approach defined by the the smart health card could be used to create the smart CRVS cards https://spec.smarthealth.cards/
Details process per CRVS Events
- Timely registration of live birth
- Late Registration of live birth TBD
- Foetal Death: TBD
- Death: TBD
- Marriage: TBD
- Ruling: Includes:
- Divorce: TBD
- Annulment: TBD
- Separation: TBD
- Adoption: TBD
- Legitimation: TBD
- Recognition: TBD
Process Management
To be discussed to which extent the standard might also define the resources that would used in the above process workflow
Here some ideas
- CRVS Case: Tracks individual cases through the registration process.
- CRVS Task: Assigns and monitors specific workflow steps.
- Person: Identifies individuals in the system.
- Practitioner: Defines user roles with authentication and authorization.
- Group: Assigns tasks to teams.
- Location: Records geographical data for events and organizations.
- Organisation: Identifies authorities involved in CRVS processes.